LangGraph Reflection
Langgraph Reflections
Section titled “Langgraph Reflections”Overview
Section titled “Overview”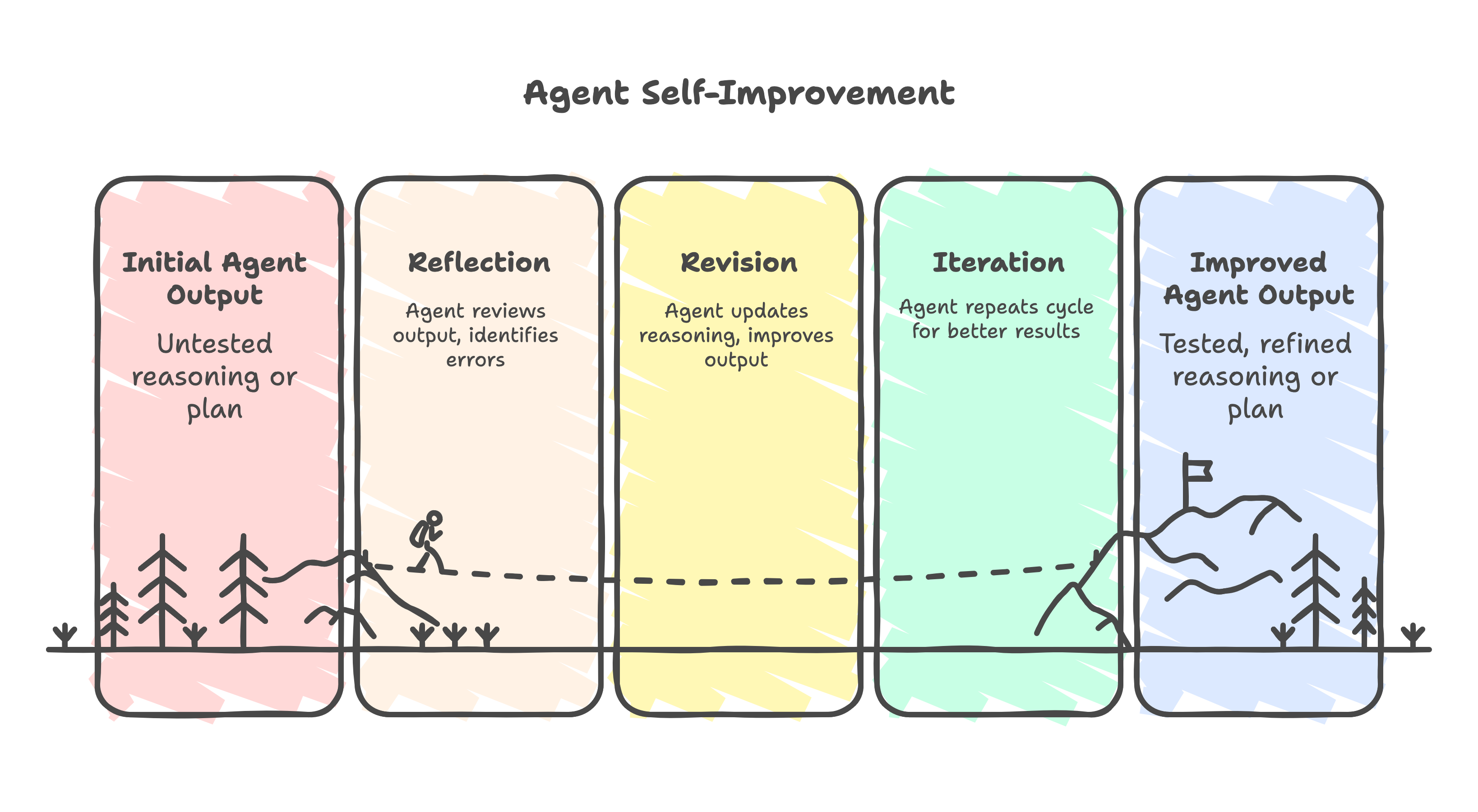
Reflection is related to agent self-improvement or reasoning feedback loops.
- Reflection is a framework-level pattern (or module) that enables an LLM agent to evaluate its own outputs, learn from mistakes, and revise or improve results across iterations.
- Reflexion: It’s an agent training framework where an LLM learns from verbal feedback (its own or from a reward model) through multiple episodes — akin to reinforcement learning (RL) but using text-based reflection.
- Language Agent Tree Search (LATS): It is a framework that combines LLMs with tree-search planning, inspired by algorithms like Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS).
Reflection
Section titled “Reflection”The agent goes through a Reflect → Revise cycle:
- Generation: The agent produces an initial answer or plan.
- Reflection: The agent reviews that output — often using another LLM call — and identifies mistakes or improvements.
- Revision: The agent updates its reasoning or final output based on the reflection.
RefleXion paper
Section titled “RefleXion paper”The agent goes through each episode involving:
- Trajectory Generation → The agent takes actions and generates an outcome.
- Reflection → The agent verbalizes what worked or failed.
- Improvement → The agent uses the reflection to guide the next episode’s reasoning or action sequence.
This process yields cumulative learning across episodes — a meta-learning approach for long-term reasoning and self-correction.
LATS lets an LLM simulate multiple reasoning paths, evaluate them, and select the best one — instead of following a single linear reasoning trace (like in ReAct or standard chain-of-thought).
Root (Question) / | \ Step A1 Step B1 Step C1 | | | ... ... ... (each branch grows via reasoning steps)Algorithmic Structure
Section titled “Algorithmic Structure”A simplified LATS loop looks like:
-
Expansion
Generate multiple next-step reasoning candidates from the current node using an LLM.
-
Evaluation
Use another LLM call (or a value function) to score each candidate by quality, correctness, or expected utility.
-
Selection / Backpropagation
Propagate scores up the tree and select the best reasoning trajectory.
-
Termination
Stop when a branch reaches a high-confidence or goal state (e.g., complete answer or solved task).