Azure Data Factory (Data Flow)
Recently I’m working in Azure to implement ETL jobs. The main tool is ADF (Azure Data Factory). This post show some solutions to resolve issue in my work.
Process CSV files and merge different system files into one file
- Source: CSV files with filename format (abcd_yyyymmdd_uuid.csv), where abcd is system id.
- a_20180101_9ca2bed1-2ed0-eaeb-8401-784f43755025.csv
- a_20180101_cca2bed1-aed0-11eb-8401-784f73755025.csv
- b_20190202_ece2bed1-2ed0-abeb-8401-784f43755025.csv
- c_20180101_ada2bed1-2ed0-22eb-8401-784f43755025.csv
- Sink: yyyymmdd.csv
- 20180101.csv
- 20190202.csv
ADF Pipeline
Section titled “ADF Pipeline”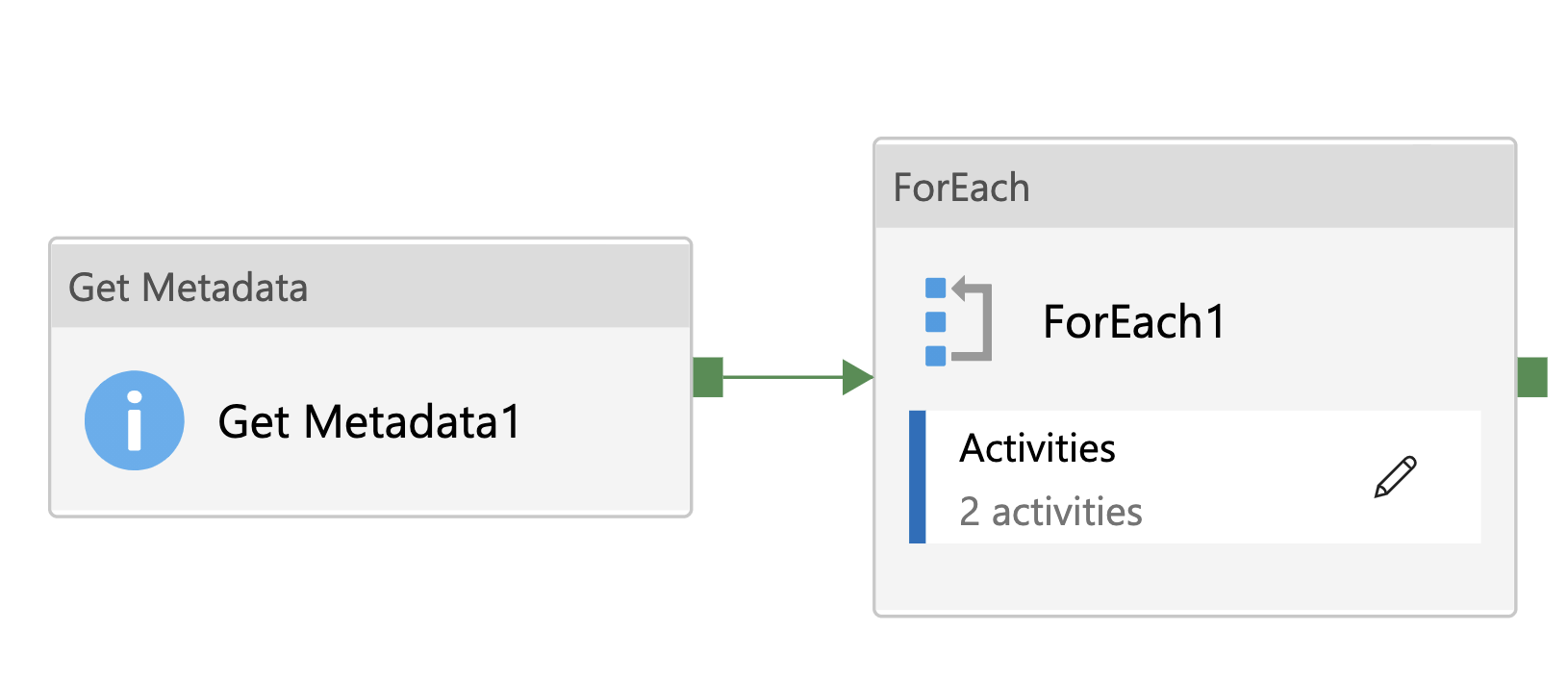
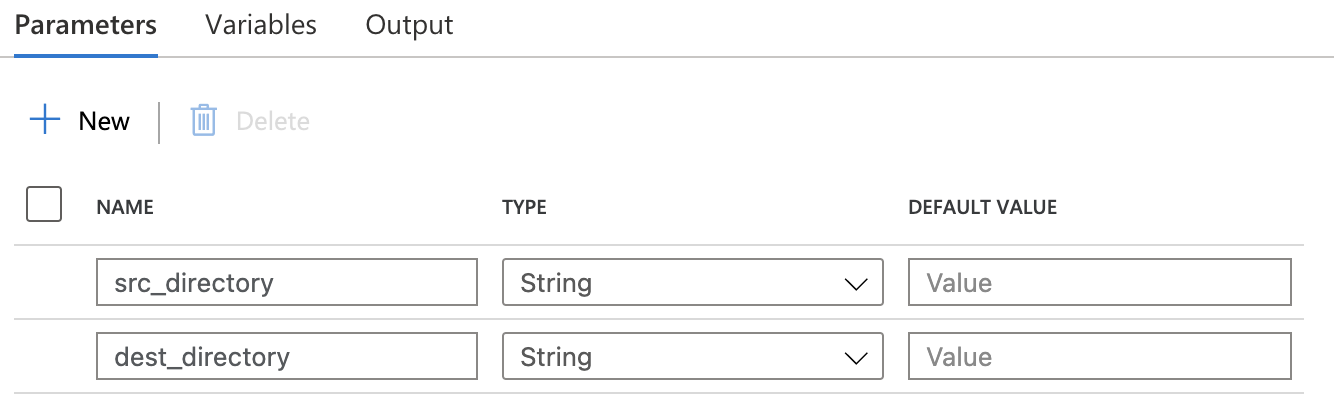
Activities
Section titled “Activities”Get Metadata
Section titled “Get Metadata”- Input: source directory/parameters
- Output: metadata of each object
Get Metadata activity iterate source directory to obtain each object. The most important one is Argument
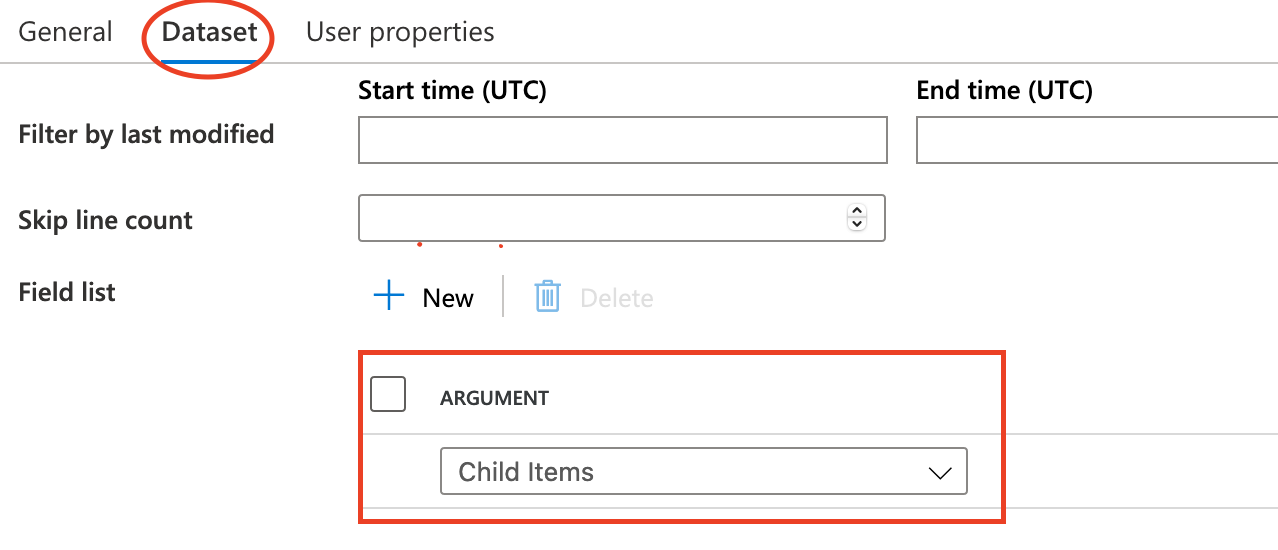
ForEach
Section titled “ForEach”- Input: output of Get Metadata
- Output: None
ForEach activity is used to process each object in source direcoty.
@activity('Get Metadata1').output.childItems
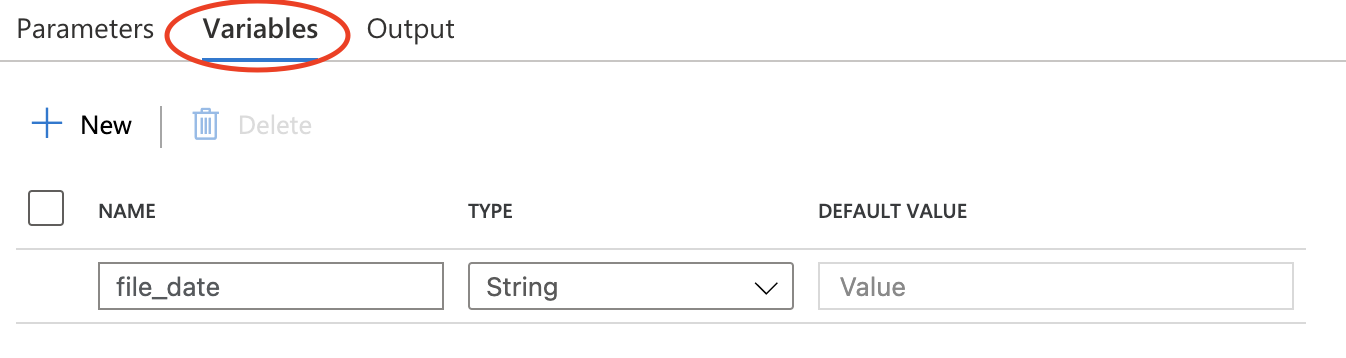
Set Variables
Section titled “Set Variables”It’s convenient to predefine a value used in next step.
Dataflow
Section titled “Dataflow”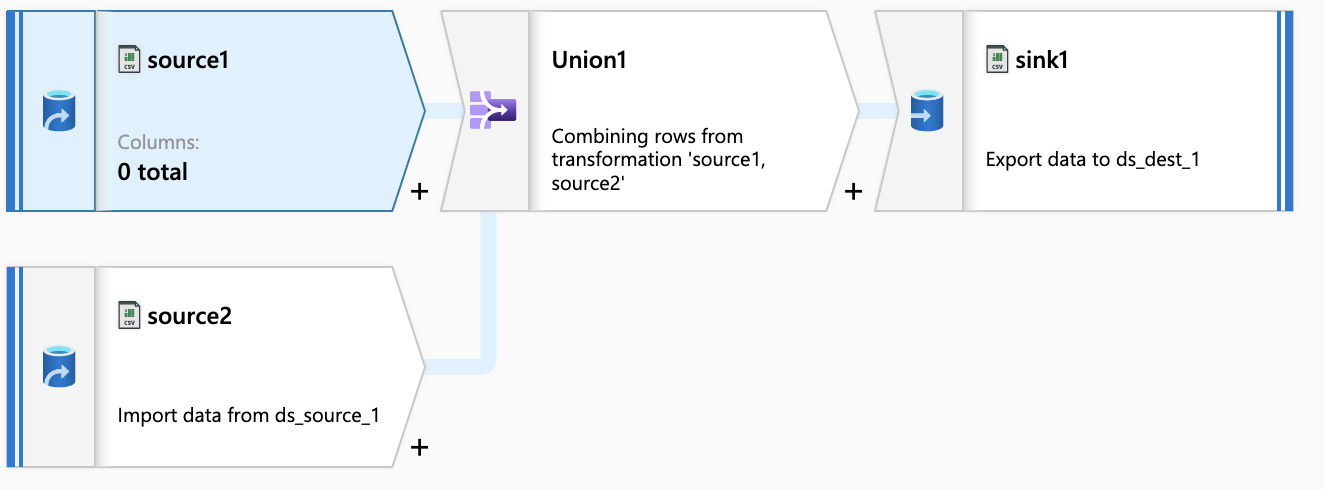
The dataflow merge all files with same date, and source1 and sink are the same destination.
So, initially source1 is empty and check this options.
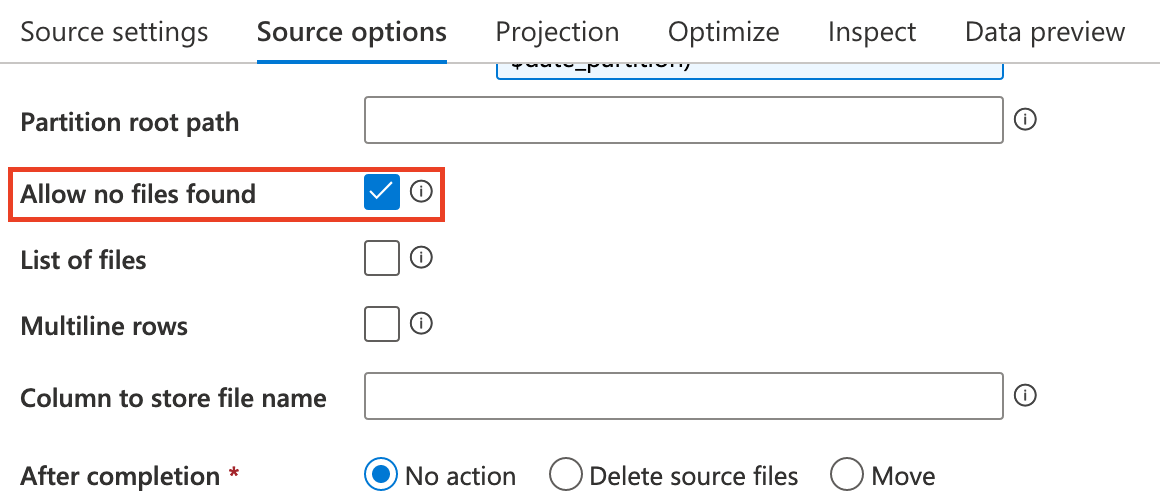
The only configuration in Sink is the File name option
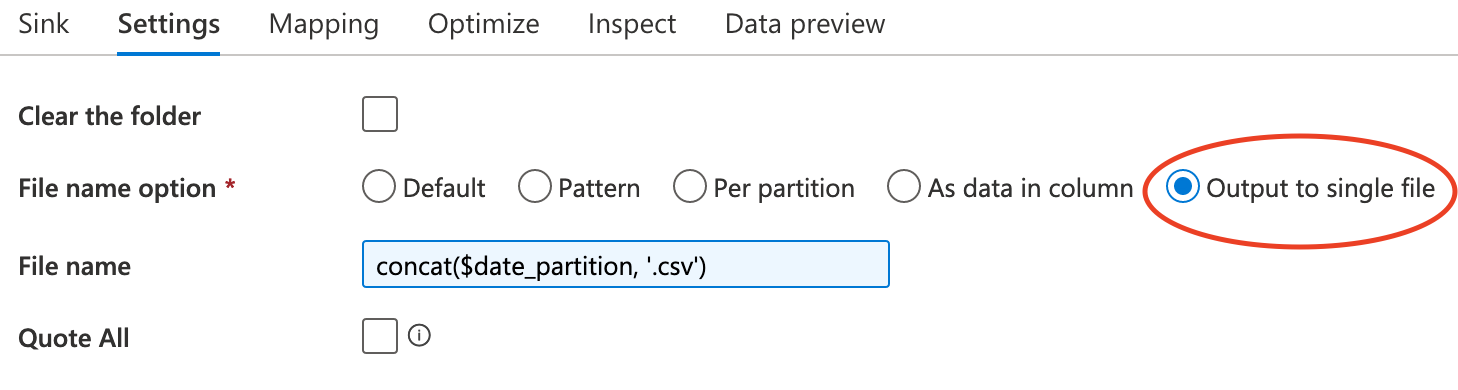
Aggregation of filenames
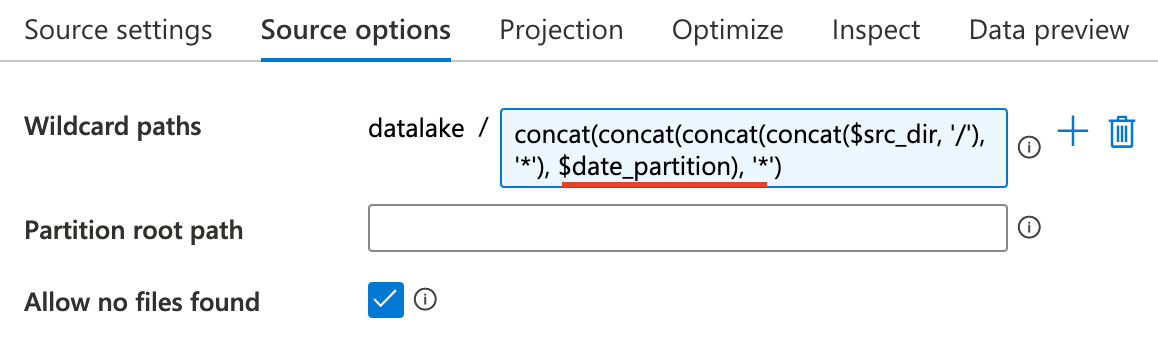
Section titled “Aggregation of filenames”The last problem in dataflow is how to merge files with same date in dataflow, which means we firstly find out all these files. The solution to this problems is regex expression.
Generally CSV file has a header and we can process it easily in ADF. However, a special case is a large CSV file has multiple different headers and we need to automatically split it into regular csv files with headers respectively.
-
Sample data:
h1,h1_col1,h1_col2,h1_col3 h2,h2_col1,h2_col2,h2_col3,h2_col4,h2_col5 h3,h3_col1,h3_col2 h1,h1_row1_1,h1_row1_2,h1_row1_3 h1,h1_row2_1,h1_row2_2,h1_row2_3 h1,h1_row3_1,h1_row3_2,h1_row3_3 h2,h2_row1_1,h2_row1_2,h2_row1_3,h2_row1_4,h2_row1_5 h2,h2_row2_1,h2_row2_2,h2_row2_3,h2_row2_4,h2_row2_5 h2,h2_row3_1,h2_row3_2,h2_row3_3,h2_row3_4,h2_row3_5 h2,h2_row4_1,h2_row4_2,h2_row4_3,h2_row4_4,h2_row4_5 h2,h2_row5_1,h2_row5_2,h2_row5_3,h2_row5_4,h2_row5_5 h3,h3_row1_1,h3_row1_2 h3,h3_row2_1,h3_row2_2
-
Explanation:
- header format: header name, columns names
- 3 headers : h1, h2 and h3
- the 1st column of each row is header name and rest of columns are values
-
Output:
- h1 file
h1_col1,h1_col2,h1_col3 h1_row1_1,h1_row1_2,h1_row1_3 h1_row2_1,h1_row2_2,h1_row2_3 h1_row3_1,h1_row3_2,h1_row3_3
- h2 file
h2_col1,h2_col2,h2_col3,h2_col4,h2_col5 h2_row1_1,h2_row1_2,h2_row1_3,h2_row1_4,h2_row1_5 h2_row2_1,h2_row2_2,h2_row2_3,h2_row2_4,h2_row2_5 h2_row3_1,h2_row3_2,h2_row3_3,h2_row3_4,h2_row3_5 h2_row4_1,h2_row4_2,h2_row4_3,h2_row4_4,h2_row4_5 h2_row5_1,h2_row5_2,h2_row5_3,h2_row5_4,h2_row5_5
- h3 file
h3_col1,h3_col2 h3_row1_1,h3_row1_2 h3_row2_1,h3_row2_2
- h1 file
Dataflow
Section titled “Dataflow”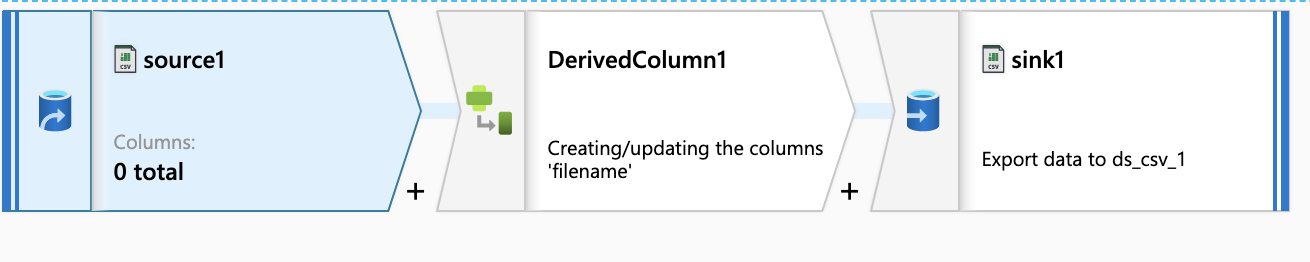
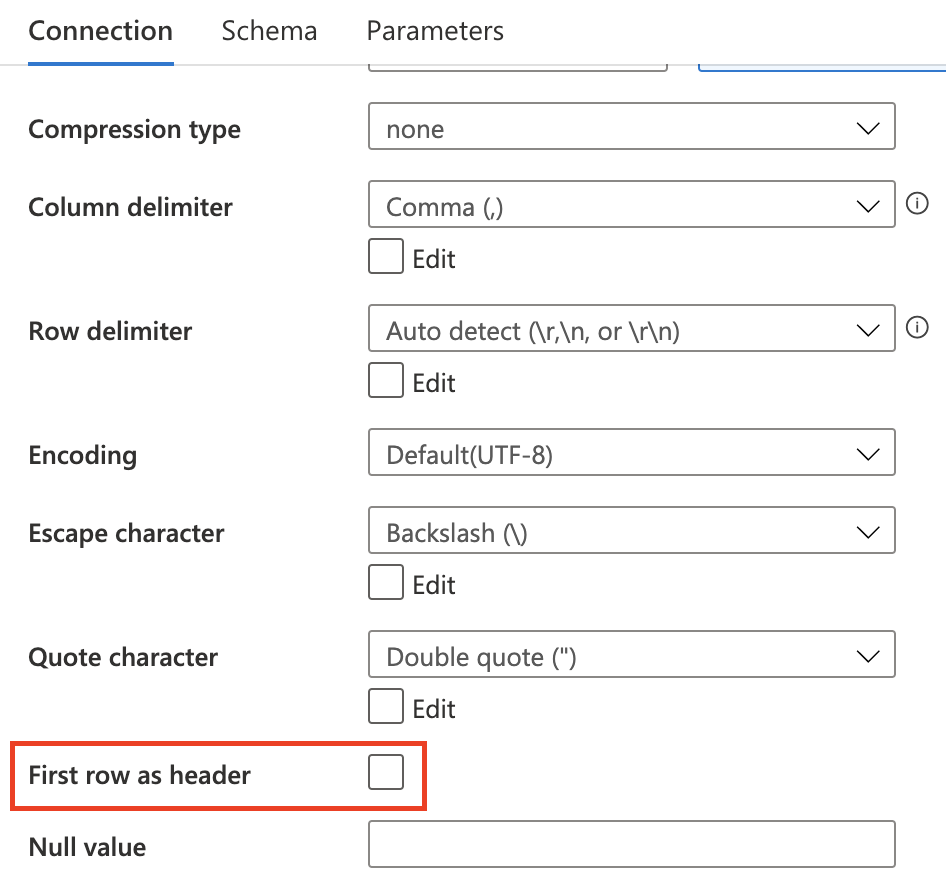
The dataset used in source and sink must uncheck this
DerivedColumn
Section titled “DerivedColumn”Because no header is in the dataset, ADF automatically assign a column name to each one. The column name format is _colindex_
In this task the header column is _col0_ and we can map this one to another name like filename
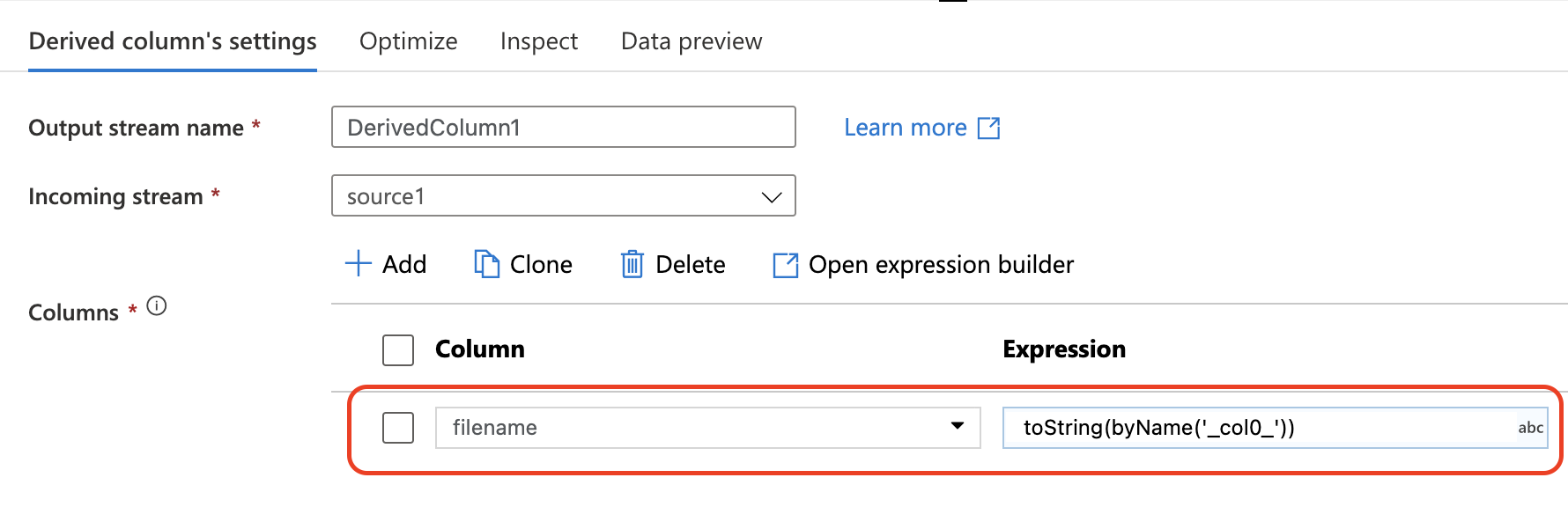
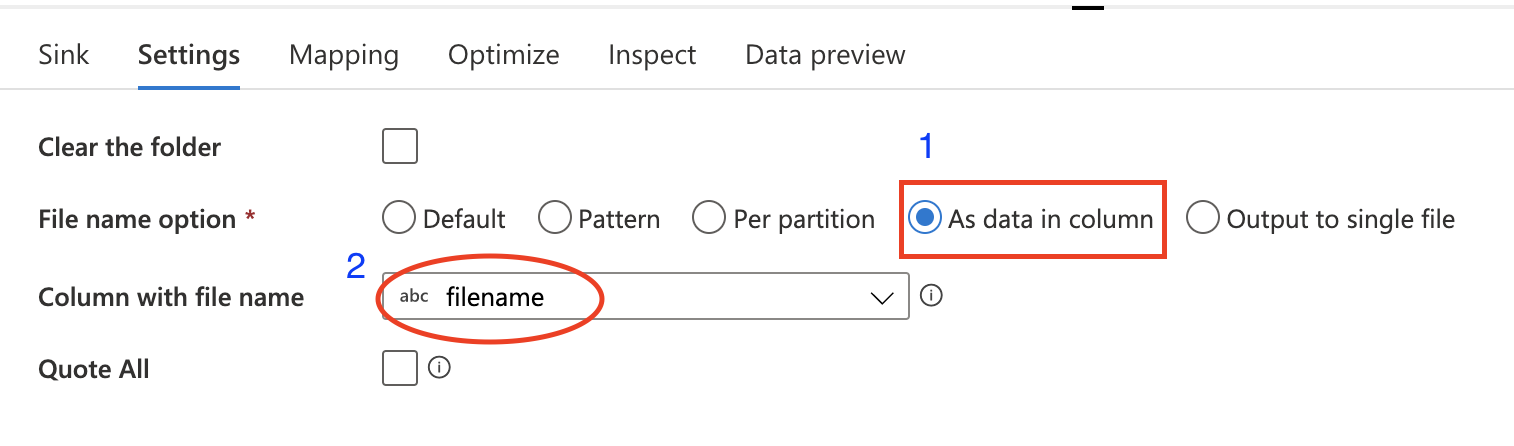
This dataflow will automatically split composite CSV file into different files and save them at container root path. To save them at another directory, you can add folder name to the mapping column name in DerivedColumn activity.
Trigger
Section titled “Trigger”We use blob event trigger to implement automation. Once uploading a new file is done, these pipeline will process it automatically. How to create event trigger
Two values in trigger are used by pipeline
- @triggerBody().folderPath : /container name/folder/
- @triggerBody().fileName : blob name
Pandas Processing
Section titled “Pandas Processing”import pandas as pdimport csv
df = pd.read_csv('sample.csv', sep='^([^,]+),',engine='python', header=None)df.drop(df.columns[0], axis=1, inplace=True)
heads = df[df.columns[0]].unique()d = dict(tuple(df.groupby(df.columns[0])))
for h in heads: outputfile = d[h] outputfile.drop(outputfile.columns[0], axis=1, inplace=True) outputfile.to_csv('{0}.csv'.format(h), sep=' ', index=False, header=False)